Did you know that car dealers can mark up your loan?
More than 60% of people don’t. And no one has quantified how much of a markup you can expect to pay. That’s why we created the Outside Financial Markup Index. We crunched the numbers to figure out the average markup on an auto loan…. and the results were shocking.
The average loan package markup: $2,109
But that’s just an average. You COULD BE PAYING MORE.
This number has been a secret until now. Bears don’t like secrets.
Here's how it works:
You pay a markup to the dealer for each loan and product arrangeD in the back office. The dealer doesn’t have to tell you you’re paying all these markups.
Loan Markup?
Dealers make a commission known as the “dealer reserve” or “finance reserve” for arranging an auto loan for a car buyer. The dealer adds 1-2% to the bank’s interest rate, which can cost hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
Dealers have no obligation to tell you how much they’re marking your loan up by.
Let’s look at some other markups….
VSC - Vehicle Service Contract
A Vehicle Service Contract (sometimes known as an extended warranty) covers the cost of certain repairs.
The right VSC can act like health insurance for your car — for a small amount each month, you can avoid major repair bills.
How much is it?
VSC prices – and markups – are all over the map.
The wholesale price of a VSC (that is, what the dealer has to pay) can change a lot depending on the vehicle you’re buying – how old it is, the reliability of that make and model, and expected repair costs. For example, a VSC for a 5 year old Mercedes will cost a lot more than one for a brand-new Honda Civic.
Markups can range from $600 to $2,000, mostly depending on how much the dealer chooses to charge.
GAP - Guaranteed Asset Protection
GAP (Guaranteed Asset Protection) Waiver policies cover the difference between what your insurance company will pay if your car is stolen or totaled and what you owe on your loan. That “gap” could cost thousands of dollars.
How much is it?
GAP Waiver rates usually depend on how long you want the coverage to last – the more months you cover, the more expensive it will be — but usually only by a few dollars.
Typical GAP prices are around $200-400, while markups on GAP can run around $200 to $600.
Ancillary Vehicle Protection
Dealers can make a lot of money by selling you a lot of ancillary products, from appearance contracts to etching packages. Some are valuable; others are no better than a can of ScotchGard.
How much is it?
Markups on appearance contracts or Tire & Wheel can range from $200 to $600, while markups on etching packages can set you back $100 to $300.
As long as your lender allows it, dealers can charge as much as they want for any product they choose.
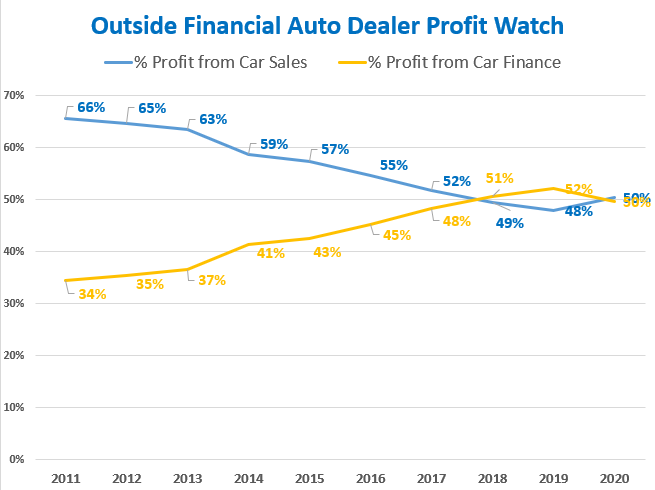
For the first time ever, dealers make as much money when they finance your car as when they sell you the car.
Where's the Money?
% Dealer Profit from Selling Cars and Financing Cars
You don’t have to pay these dealer markups.
You can save thousands of dollars by arranging your loan BEFORE you go to the dealership.
We started this company because the car financing process is broken and unfair, and the Outside Financial Markup Index proves the point. By arranging your auto loan BEFORE you go to the dealership, you can choose what's right for you, on your time, at your pace, in your place. No stress. No "let me check with the manager" games. No undisclosed $2,109 markups.
Our sources
SEC filings from public financial institutions, auto manufacturers, and auto dealers
Industry data sources and periodicals, including the National Automobile Dealers Association, Experian, DealerStrong, and Auto Finance News
Interviews with dozens of industry professionals
Research conducted by consumer protection groups, including the National Consumer Law Center and the Center for Responsible Lending
Government enforcement actions against captive lenders, auto dealerships, and banks
CFPB Consent Orders against captive auto finance companies, independent auto finance companies, large national banking institutions, and auto dealerships
Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Proprietary Outside Financial survey (n=600)